In today’s fast-paced business world, companies generate massive amounts of data every day. Understanding this data and turning it into actionable insights is no longer optional – it’s essential. Business Intelligence (BI) is the framework that helps organizations collect, analyze, and interpret data to make smarter decisions.
This guide will walk you through BI step by step, explaining key concepts, tools, and strategies in simple, clear language. By the end, you’ll understand how businesses leverage BI to stay ahead of the competition, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions that support growth.
What is Business Intelligence?
Business Intelligence is the process of transforming raw data into meaningful insights that drive better decisions. It combines data collection, analysis, visualization, and reporting to help organizations understand their operations, customers, and markets.
BI integrates information from multiple sources such as databases, ERP systems, CRM tools, and even online interactions. It is not just about reporting; it’s about identifying trends and patterns that inform strategic decisions. With BI, leaders can make data-driven choices rather than relying solely on intuition.
For example, a retail company can use BI to track which products sell best, which regions perform well, and where operational improvements are needed. By analyzing customer purchase patterns, businesses can optimize their inventory, tailor marketing strategies, and improve customer satisfaction. In essence, BI acts like a pair of glasses that helps companies clearly see their performance, uncover opportunities, and act strategically.
Why Do Businesses Need Business Intelligence?
Many organizations collect data, but without proper analysis, data alone provides little value. BI allows companies to extract meaning from complex information and make faster, smarter decisions.
Some key benefits of BI include:
- Faster decision-making: Access to real-time data allows leaders to respond quickly to changing conditions.
- Operational efficiency: Identify inefficiencies and optimize processes to reduce costs and improve productivity.
- Customer insights: Understand customer behavior, preferences, and trends for more effective targeting.
- Competitive advantage: Spot emerging trends and market opportunities before competitors.
- Predictive capabilities: Use historical data to forecast sales, demand, and potential risks.
Without BI, organizations risk making decisions based on incomplete information or assumptions, which can lead to inefficiencies, lost revenue, and missed opportunities. BI allows businesses to move from reactive strategies to proactive planning, ensuring data works as a strategic asset.
For instance, a company noticing a decline in sales for a specific product can quickly analyze why demand dropped, adjust pricing or marketing, and prevent further losses. Similarly, BI can help operations teams monitor supply chain performance, identify delays, and optimize logistics for better efficiency.
Key Components of Business Intelligence
A successful BI system has several components that work together to make data actionable.
- Data Sources: These are the origins of information, including databases, CRM systems, ERP platforms, social media, and IoT devices.
- Data Warehousing: A central repository where data from multiple sources is stored and organized for analysis.
- ETL Processes (Extract, Transform, Load): These processes clean, format, and consolidate raw data so it can be effectively analyzed.
- Analytics Tools: Software applications that allow users to query data, create reports, and uncover insights.
- Visualization Layer: Dashboards, charts, and graphs that make data easy to interpret and share across teams.
Together, these components ensure a smooth flow of data from collection to decision-making. A well-structured BI framework allows organizations to scale as data volumes increase and adapt as business needs evolve.
For example, a company using BI can combine sales data from multiple regions, analyze it for trends, and visualize performance in an intuitive dashboard. This approach enables management to make decisions quickly and with confidence.
How Does Business Intelligence Improve Decision-Making?
Business Intelligence affects almost every aspect of a business by providing actionable insights. With BI, leaders can make informed decisions, identify operational inefficiencies, understand customer behavior, and anticipate market trends.
For instance, marketing teams can use BI to analyze customer demographics and purchasing habits, tailoring campaigns to maximize engagement. Operations teams can spot bottlenecks in production or distribution, helping streamline processes. Finance departments can use BI to forecast revenue, monitor expenses, and optimize budgets.
BI moves organizations from reactive decision-making to proactive strategies. Instead of relying solely on historical reports, businesses can predict future outcomes, reduce uncertainty, and act strategically. This proactive approach improves overall performance, reduces costs, and enhances customer satisfaction.
In addition, BI fosters collaboration across departments. By sharing insights and dashboards, teams can align their goals, monitor performance, and work toward common objectives. This holistic perspective ensures decisions are not made in silos but are informed by data from across the organization.
Business Intelligence tools help organizations analyze data, generate reports, and visualize insights for better decision-making. The right BI tools depend on business size, data complexity, and the technical skills of the team
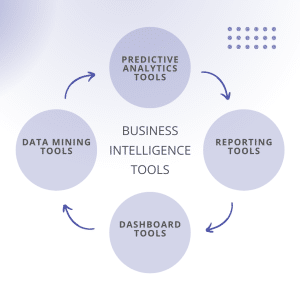
Reporting Tools
These tools convert raw data into structured reports and summaries. They help businesses understand performance, track progress, and identify gaps through scheduled or on-demand reports.
Dashboard Tools
Dashboards present key metrics and trends in a visual, easy-to-read format. They enable quick monitoring of KPIs such as sales, revenue, and operational efficiency in real time.
Data Mining Tools
Data mining tools analyze large datasets to uncover hidden patterns and relationships. They are useful for discovering customer behavior, anomalies, and trends that are not immediately visible.
Predictive Analytics Tools
These tools use historical data and statistical models to forecast future outcomes. Businesses use them to predict demand, revenue, risks, and operational challenges in advance.
Why the Right BI Tools Matter
Using the right combination of BI tools simplifies complex data and reduces decision-making time. Small businesses often focus on simple dashboards, while large enterprises use advanced analytics integrated with ERP and CRM systems.
With effective BI tools in place, data becomes a strategic asset—helping businesses act faster, plan smarter, and stay competitive.
Business Intelligence: Advanced Insights and Implementation
As businesses grow, so does the volume of data they generate. Business Intelligence (BI) is not just about analyzing historical data- it’s about applying insights strategically to predict trends, optimize operations, and improve decision-making. Part 2 of this guide explores advanced aspects of BI, including predictive analytics, real-time dashboards, implementation strategies, future trends, and measuring success.
Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics in Business Intelligence
Predictive analytics is a powerful component of modern BI. It uses historical data to forecast potential outcomes, helping organizations make informed decisions. By identifying patterns and correlations, predictive analytics enables businesses to anticipate customer behavior, optimize inventory, and plan marketing campaigns more effectively.
Prescriptive analytics takes this a step further. Instead of simply predicting what might happen, it recommends actions that can maximize positive outcomes or mitigate risks. For instance, a retail company could use prescriptive analytics to determine the optimal pricing strategy during peak seasons or decide which marketing campaigns will generate the highest return.
Together, predictive and prescriptive analytics transform BI from a descriptive tool into a forward-looking decision-making framework. Businesses can move from merely understanding past performance to actively shaping future outcomes, gaining a significant competitive advantage.
Real-Time Dashboards: Seeing Your Business in Action
Real-time dashboards are an essential part of BI that provide instant insights into business performance. Unlike traditional reports that rely on historical data, real-time dashboards update continuously, giving organizations a live view of their operations.
These dashboards allow managers and executives to monitor sales, production, customer interactions, and financial metrics simultaneously. By visualizing data as it happens, companies can respond quickly to unexpected changes, avoid potential issues, and seize emerging opportunities.
Real-time dashboards also promote collaboration. Teams across departments can access the same data, align strategies, and make decisions based on a unified understanding of performance. This shared visibility ensures that decision-making is consistent, timely, and supported by accurate data.
How Can Businesses Implement Business Intelligence Effectively?
Successful BI implementation requires careful planning, collaboration, and alignment with business objectives. The process begins with understanding what insights are needed and identifying the sources of relevant data. Without clear goals, even the most sophisticated BI tools will fail to deliver value.
Once goals are defined, organizations should focus on building a reliable data infrastructure. This involves integrating data from various sources, ensuring data quality, and establishing governance practices to maintain accuracy and security. Data warehousing, ETL processes, and automated workflows play critical roles in this phase.
After the infrastructure is in place, selecting the right BI tools is essential. Businesses must consider usability, scalability, and compatibility with existing systems. Training teams to interpret and leverage BI insights effectively is equally important, as the value of BI lies in informed action, not just reporting.
Finally, BI implementation should be iterative. Organizations should continuously monitor performance, refine processes, and adjust strategies as needed. By adopting a phased approach, businesses can minimize risks, maximize adoption, and ensure long-term success.
Trends Shaping the Future of Business Intelligence
The BI landscape is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and growing demands for data-driven decision-making. One notable trend is the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into BI platforms. AI-powered analytics can identify patterns that humans may overlook, automate routine reporting, and provide deeper predictive insights.
Cloud-based BI solutions are also transforming the industry. They allow businesses of all sizes to access scalable, cost-effective analytics without investing heavily in infrastructure. Cloud BI enables faster deployment, real-time collaboration, and easier integration with other digital tools.
Self-service BI is another growing trend. Non-technical users can access dashboards, generate reports, and explore data independently, reducing dependency on IT teams. Additionally, the rise of data storytelling emphasizes presenting insights in a compelling, understandable manner, making BI outputs more actionable.
These trends indicate that future BI will be more intelligent, accessible, and integral to business strategy, empowering organizations to make proactive decisions rather than reactive ones.
Measuring the Success of Business Intelligence Initiatives
The ultimate goal of BI is to improve business performance, but measuring its success can be challenging. Organizations should define clear metrics that align with strategic objectives, such as increased revenue, improved operational efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, or reduced costs.
Effective measurement goes beyond tracking dashboard usage or report generation. It involves evaluating whether BI insights lead to tangible decisions and outcomes. For example, if a company implements BI-driven supply chain optimizations, success can be measured by reduced delivery times, lower inventory costs, and improved service levels.
Continuous assessment is critical. BI systems and business needs evolve over time, so organizations must regularly review performance, update key metrics, and refine analytical models. By combining quantitative results with qualitative feedback from stakeholders, businesses can ensure that their BI initiatives remain valuable and relevant.
Ultimately, measuring success is not just about ROI- it’s about demonstrating how data-driven decisions improve the organization’s agility, competitiveness, and long-term growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does business intelligence help companies make better decisions?
Business intelligence analyzes data from different sources and converts it into clear insights. This helps leaders make informed decisions based on facts instead of guesswork.
Why is business intelligence important for growing businesses?
As data increases, BI helps businesses track performance, identify trends, and avoid costly mistakes. It ensures data supports growth rather than creating confusion.
What is the role of business intelligence in understanding customer behavior?
BI helps analyze customer data such as purchase patterns and preferences. This allows businesses to personalize marketing and improve customer satisfaction.
How does business intelligence improve operational efficiency?
By highlighting inefficiencies and bottlenecks, BI enables teams to optimize processes. This reduces costs, saves time, and improves overall productivity.
What makes business intelligence different from traditional reporting?
Traditional reporting shows past data, while BI reveals trends and insights. BI helps businesses act proactively rather than reacting after problems occur.
How do real-time dashboards support faster decision-making?
Real-time dashboards show live business performance metrics. This allows teams to respond quickly to changes and make timely decisions.
How can businesses evaluate the success of their business intelligence strategy?
Success is measured by how BI insights improve decisions and outcomes. Better efficiency, growth, and clarity indicate an effective BI strategy.


