Data analytics is the process of using data to understand what is happening, why it is happening, and what may happen next. Every digital activity creates data. When someone visits a website, makes a payment, uses an app, or interacts with a system, data is generated. Data analytics turns this raw information into meaningful insights that people and businesses can actually use.
At its core, data analytics helps answer simple but important questions. What is working well? What is not working? Where are problems coming from? What opportunities exist that are not visible on the surface? Instead of relying on guesswork or assumptions, decisions are made using facts derived from data.
In the early days, data was small and manageable. Today, organizations deal with massive volumes of data coming from multiple sources. This is where modern data analytics becomes essential. It provides structured methods to collect, organize, analyze, and interpret data so that it supports better decision-making.
Data analytics is not limited to technology companies. It is used across industries such as retail, healthcare, finance, manufacturing, logistics, education, and government. Any organization that wants to improve performance, reduce risk, or understand behavior can benefit from data analytics.
Why Data Analytics Has Become Essential Today
In the modern world, data is growing faster than ever before. Every business operation produces data, from customer interactions to internal processes. Without analytics, this data remains unused and often overwhelming. Data analytics helps convert this growing volume of information into clarity.
One major reason data analytics is important today is speed. Markets change quickly, customer expectations evolve, and competition increases constantly. Decisions must be made faster and with greater confidence. Data analytics supports real-time and near real-time insights, allowing organizations to respond quickly instead of reacting too late.
Another reason is accuracy. Human intuition alone is not enough when dealing with complex systems and large datasets. Data analytics reduces bias by relying on evidence rather than assumptions. This leads to more consistent and reliable decisions.
Data analytics also supports long-term planning. By studying patterns and trends, organizations can prepare for future outcomes instead of only reacting to past events. This forward-looking approach is especially important in uncertain and competitive environments.
As data becomes central to operations, data analytics moves from being a support function to a core capability. Organizations that adopt it effectively gain a strong advantage over those that do not.
Understanding Different Types of Data and Data Sources
To understand data analytics properly, it is important to know what kind of data exists and where it comes from. Data can appear in many forms and structures, and each type requires a different approach to analysis.
Structured data is organized in fixed formats like tables and databases. It includes things such as customer records, transaction details, and inventory information. This data is easier to analyze because it follows clear rules.
Unstructured data does not have a fixed format. Examples include text files, emails, images, videos, and social media content. A large portion of modern data falls into this category, making analytics more complex.
Semi-structured data lies between structured and unstructured data. It may not follow strict tables but still contains patterns, such as system logs or data stored in JSON formats.
Data comes from websites, mobile apps, sensors, enterprise systems, cloud platforms, and digital services. One of the world’s biggest sources of big data today is continuous digital interaction across platforms and devices.
The Role of Big Data in Modern Data Analytics
Big data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that traditional tools cannot handle efficiently. These datasets are characterized by large volume, fast generation speed, and multiple data formats. Big data analytics focuses on extracting value from this complexity.
Big data is important because many valuable insights only appear when large datasets are analyzed together. Customer behavior, system performance, fraud detection, and operational efficiency often depend on big data analysis.
To manage this scale, organizations rely on big data platforms and big data stacks. These systems are designed to store, process, and analyze data efficiently while maintaining performance and reliability.
It is important to understand that big data alone does not create value. The value comes from applying the right analytics techniques to extract meaningful insights that support decision-making.
How Data Analytics Gradually Creates Real Business Impact
Data analytics creates impact through a gradual process rather than instant results. It starts with collecting data, followed by cleaning, organizing, analyzing, and interpreting it. Each step adds clarity and reliability to the insights generated.
In early stages, analytics focuses on understanding what has already happened. As maturity increases, it helps explain why outcomes occurred. Over time, analytics enables predictive analytics, allowing organizations to anticipate future outcomes based on patterns and trends.
The real impact of data analytics appears when insights are translated into actions. Reports and dashboards are useful, but value is created when decisions improve, processes become efficient, and results are measurable.
Data analytics is not a one-time activity. It is a continuous capability that grows as data quality improves and experience increases.
How Does Data Analytics Move from Raw Data to Useful Insights?
After understanding what data analytics is and why it matters, the next step is learning how raw data actually becomes meaningful insights. Raw data by itself is messy, incomplete, and often unusable. Data analytics introduces structure and logic so that data can support real decisions.
The process begins once data is collected from different sources. This data may come from applications, databases, websites, sensors, or cloud platforms. Because data arrives in different formats and quality levels, it cannot be analyzed immediately. It must go through preparation before analysis begins.
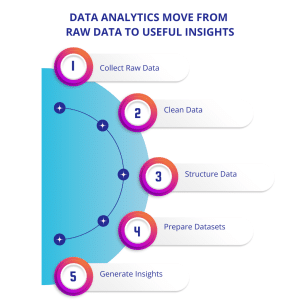
Collect Raw Data
Data is gathered from applications, databases, websites, sensors, and cloud platforms. Collecting all relevant sources ensures a complete foundation for analysis.
Clean Data
Raw data often contains errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies. Cleaning the data improves accuracy and builds trust in the insights that follow.
Structure Data
Data is organized into tables, formats, or models suitable for analytics tools. Proper structuring allows patterns to be identified effectively.
Prepare Datasets
Prepared datasets are ready for dashboards, reports, or Machine Learning models. This step ensures data can be used immediately for analysis and decision-making.
Generate Insights
The final processed data is transformed into actionable business insights. Teams can use these insights to make informed, strategic decisions.
What Role Do Data Pipelines and ETL Play in Analytics?
Behind every successful data analytics system is a well-designed data pipeline. A data pipeline is the path data follows from its source to its final destination, such as a dashboard or analytics model. One of the most important concepts in this flow is the ETL pipeline.
ETL stands for extract, transform, and load. It describes how data is taken from source systems, transformed into usable formats, and loaded into storage systems for analysis. ETL pipeline architecture ensures that data flows reliably and consistently.
The importance of ETL and data pipelines can be seen in:
- Managing data from multiple sources efficiently
- Ensuring data consistency and accuracy
- Supporting analytics at scale
- Enabling automation in data processing
Modern data analytics environments often use automated data pipelines to reduce manual work and errors. These pipelines support real-time and batch processing depending on business needs.
Without proper data pipelines, analytics becomes slow, unreliable, and difficult to maintain. Data pipelines form the backbone of any scalable data analytics system.
Understanding Data Warehouses and Their Role in Analytics
Once data is processed through pipelines, it needs a place to be stored for analysis. This is where data warehouses come into play. A data warehouse is a centralized system designed specifically for storing and analyzing large volumes of structured data.
Unlike operational databases, data warehouses are optimized for analytics rather than transactions. They support complex queries, historical analysis, and large-scale reporting without affecting operational systems.
There are different data warehouse models depending on use cases and data volume. The data warehouse design process focuses on organizing data in a way that supports fast and reliable analytics. Over time, data warehousing in the real world has evolved to support both traditional and modern analytics needs.
Data warehouses are especially useful when organizations want consistent reporting across teams. They provide a single source of truth, reducing confusion caused by conflicting data from different systems.
Understanding data warehouses is essential because they sit at the center of many analytics ecosystems, connecting raw data to insights.
Data Visualization and Dashboards as the Analytics Interface
Data analytics is only valuable if insights can be understood easily. This is where data visualization plays a critical role. Data visualization converts numbers and metrics into charts, graphs, and visual patterns that humans can interpret quickly.
Dashboards act as the main interface between data and decision-makers. A data analytics dashboard presents key metrics in a clear and organized format. Dynamic dashboards allow users to interact with data, filter views, and explore insights without technical expertise.
Effective visualization focuses on clarity rather than complexity. The goal is to highlight what matters most and guide attention toward important trends or issues. Poor visualization can confuse users and reduce trust in analytics.
Dashboards are widely used across teams such as operations, marketing, finance, and leadership. They help monitor performance, track progress, and identify issues early.
Visualization bridges the gap between technical analytics and business understanding, making insights accessible to everyone.
Real-Time Analytics and the Difference Between Analysis and Reporting
Traditional analytics often focuses on historical data, analyzing what has already happened. Real-time data analytics expands this capability by analyzing data as it is generated. This allows organizations to respond immediately instead of waiting for reports.
Real-time analytics is especially important in scenarios where timing matters, such as monitoring systems, detecting anomalies, or responding to customer actions. It supports faster decisions and proactive responses.
It is also important to understand the difference between analysis and reporting. Reporting focuses on presenting predefined metrics, often in static formats. Analysis goes deeper by exploring data, identifying causes, and uncovering insights.
Analysis vs reporting in big data environments highlights the shift from simply viewing data to actively understanding it. Modern analytics systems support both, but analysis drives greater value.
As organizations mature, they move from basic reporting toward advanced analytics that support forecasting, optimization, and strategic planning.
How Does Predictive Analytics Build on Basic Data Analytics?
Once organizations become comfortable with understanding past and present data, the next natural step is predicting what may happen in the future. Predictive analytics uses historical data, patterns, and statistical techniques to estimate future outcomes. This is not guesswork. It is a structured approach based on evidence.
Predictive analytics helps answer questions related to demand, risk, behavior, and performance. Instead of reacting after events occur, organizations can prepare in advance and take preventive actions.
Predictive analytics typically builds on:
- Clean and well-structured historical data
- Strong data pipelines and analytics foundations
- Statistical models and machine learning techniques
- Continuous feedback to improve accuracy over time
This type of analytics is widely used in areas such as forecasting sales, identifying potential issues, planning resources, and improving customer experiences. Predictive analytics does not replace human judgment but strengthens it by adding data-driven foresight.
As analytics maturity grows, predictive capabilities become more reliable and valuable.
What Are the Main Components of Modern Big Data Analytics Systems?
Modern data analytics systems are designed to handle scale, speed, and complexity. These systems go beyond simple databases and reporting tools. They combine multiple components that work together to process and analyze large volumes of data efficiently.
A modern big data analytics environment typically includes:
- Data ingestion systems that collect data from multiple sources
- Big data platforms designed to store and process large datasets
- Stream data models that support continuous data flow
- Analytics engines that perform analysis and transformations
- Visualization layers that present insights clearly
Big data stacks allow organizations to scale analytics as data grows. They support both batch analytics and real-time data analytics depending on the use case. Understanding the main components of big data helps organizations design systems that are flexible and future-ready.
These systems form the technical backbone of advanced data analytics.
The Role of Data Engineering in Analytics Success
Data engineering plays a critical role in making data analytics work effectively. While analytics focuses on insights and interpretation, data engineering focuses on building and maintaining the systems that supply reliable data.
Data engineering concepts include designing data pipelines, managing ETL pipeline architecture, ensuring data quality, and optimizing performance. Data engineers work behind the scenes to ensure that analytics teams have access to accurate and timely data.
Modern analytics environments rely heavily on data engineering technologies to support automation and scalability. As data sources increase and analytics becomes more complex, strong data engineering becomes essential.
Without proper data engineering, analytics efforts often fail due to poor data quality, broken pipelines, or inconsistent results. Data engineering ensures that analytics systems remain stable and trustworthy over time.
In real-world environments, analytics success is deeply connected to the strength of data engineering foundations.
Analytics Maturity and Building a Long-Term Data Strategy
Data analytics maturity develops gradually. Organizations usually start with basic reporting and slowly move toward advanced analytics as skills, tools, and data quality improve. Understanding this progression helps set realistic expectations.
Early-stage analytics focuses on visibility and basic insights. As maturity grows, analytics becomes more integrated into decision-making processes. Eventually, analytics supports strategic planning, automation, and optimization.
A long-term data analytics strategy focuses on people, processes, and technology. It ensures that analytics initiatives align with organizational goals and evolve as needs change. This strategy also considers governance, data quality, and sustainability.
Analytics maturity is not about adopting the latest tools quickly. It is about building reliable systems, developing skills, and embedding analytics into everyday decisions.
Organizations that approach analytics strategically gain long-lasting value rather than short-term results.
The Future of Data Analytics and Continuous Evolution
Data analytics is continuously evolving as data sources, technologies, and expectations change. Real-time analytics, automation, and advanced modeling are becoming more common across industries.
Future analytics environments will focus more on speed, accessibility, and intelligence. Insights will reach users faster, and analytics will become more embedded into applications and workflows. This evolution makes analytics more proactive rather than reactive.
As data volumes grow and systems become more interconnected, analytics will play a central role in guiding decisions across all levels. Continuous learning and improvement will remain essential as analytics capabilities expand.
The future of data analytics is not about replacing humans but empowering them with better understanding and foresight.
Conclusion: Bringing the Complete Data Analytics Journey Together
Data analytics is a journey that starts with understanding data and gradually evolves into advanced insight-driven decision-making. In this pillar, we explored data analytics from the ground up, beginning with basic concepts and progressing toward modern analytics systems and future readiness.
We learned how data is created, structured, and analyzed, how big data and data pipelines support scale, and how dashboards and visualization make insights accessible. We also examined predictive analytics, data engineering, and long-term analytics maturity.
FAQ : Frequently Asked Questions
What does a complete data analytics lifecycle look like in real-world organizations?
The data analytics lifecycle typically includes data collection, data extraction, data cleansing, data engineering, analysis, visualization, and continuous optimization aligned with business goals.
How do businesses choose the right data analytics solutions for different use cases?
Organizations evaluate data volume, data velocity, business objectives, and existing infrastructure before selecting analytics solutions, big data platforms, or data warehouse models.
Why is data engineering considered the foundation of effective analytics?
Data engineering ensures reliable ETL pipelines, scalable architectures, and high-quality data, which are essential for consistent analytics outcomes and advanced insights.
How do big data analytics services differ from traditional analytics services?
Big data analytics services handle high-volume and real-time data streams, while traditional analytics focuses on structured, historical datasets for reporting and business intelligence.
What role does a data warehouse play in modern data analytics strategies?
A data warehouse supports structured analysis, standardized reporting, and performance tracking, often working alongside big data and real-time analytics platforms.


