Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming how businesses analyze data, automate processes, and make decisions. Yet many organizations struggle because they jump into tools without first understanding the fundamentals. A strong foundation helps businesses avoid confusion, reduce risks, and extract real value from AI initiatives.
This guide explains AI and Machine Learning step by step, using simple language and real-world logic. It starts with core concepts and gradually builds toward how intelligent systems actually function inside business environments.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Explained Simply
Artificial Intelligence refers to systems designed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from experience, identifying patterns, reasoning through information, and making decisions based on available data. Artificial Intelligence does not imply human-like consciousness. Instead, it focuses on intelligent behavior driven by data and algorithms.
Machine Learning is a subset of Artificial Intelligence that enables systems to learn from data rather than follow fixed instructions. Instead of coding rules for every possible scenario, Machine Learning models identify patterns within historical data and apply those patterns to new situations. As more data becomes available, the system improves automatically.
In business contexts, Artificial Intelligence defines what a system is capable of doing, while Machine Learning determines how accurately and efficiently it performs those tasks over time. For example, an AI system may be designed to forecast demand, but Machine Learning improves forecast accuracy as sales data, customer behavior, and seasonal trends evolve.
Together, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning enable businesses to move beyond static automation toward adaptive systems that continuously improve and respond to change.
What Is a Dataset in Machine Learning and Why Is It Important?
A dataset in Machine Learning is a structured collection of data used to train, evaluate, and refine learning models. Datasets may include numerical values, text, images, transaction histories, sensor readings, or behavioral data depending on the application.
Datasets are the foundation of Machine Learning. The quality of data directly influences the quality of outcomes. Incomplete, biased, or inconsistent datasets lead to unreliable predictions, regardless of how advanced the algorithm may be.
Machine Learning systems typically rely on different stages of data usage, including training data to learn patterns, validation data to fine-tune performance, and test data to evaluate accuracy in real-world conditions. Validation data in Machine Learning plays a particularly important role because it ensures the model generalizes well instead of memorizing historical examples.
For businesses, this means investing time in data preparation, cleansing, and organization is essential. Strong datasets create reliable insights, reduce risk, and support better decision-making across departments.
How Data Flows Through an AI System From Input to Action
An Artificial Intelligence system creates value by transforming raw data into decisions through a clearly defined flow. This flow ensures that insights are not isolated technical outputs but are directly connected to real business actions.
The process begins with data input, where information is collected from operational systems, customer interactions, sensors, or third-party sources. This data is rarely ready for use in its original form. Preprocessing standardizes formats, removes inconsistencies, and prepares data so that Machine Learning models can interpret it correctly.
Once prepared, data enters the learning or inference stage. During training, models analyze historical data to identify patterns and relationships. In production environments, trained models apply this learning to new data to generate predictions, classifications, or recommendations. These outputs are then evaluated within a business context rather than being used in isolation.
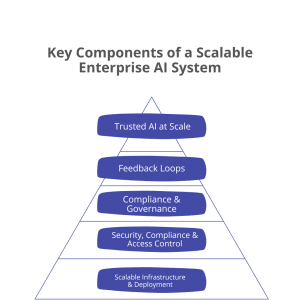
Scalable Infrastructure
A strong infrastructure provides the computing power and flexibility needed to support AI workloads. Cloud and modular systems allow models to scale across teams and use cases. This foundation enables growth without frequent redesign.
Security & Access Control
AI systems must protect sensitive data and models from unauthorized access. Role-based controls and secure environments reduce operational risk. Strong security builds trust in AI-driven decisions.
Compliance & Governance
Governance ensures AI systems follow regulatory, ethical, and organizational standards. Clear policies define accountability and responsible model usage. This reduces risk as AI adoption expands.
Continuous Monitoring & Feedback
Ongoing monitoring tracks accuracy, bias, and performance over time. Feedback from real-world outcomes helps models adapt to change. This prevents performance degradation and unexpected behavior.
Trusted AI at Scale
When all layers work together, AI becomes reliable and enterprise-ready. Decisions remain accurate, transparent, and aligned with business goals. This enables confident, large-scale AI adoption.
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms and Their Business Use
Machine Learning algorithms are designed to address different types of problems. Understanding these categories helps businesses select appropriate solutions based on data availability and business objectives.
Common categories of Machine Learning algorithms include:
- Supervised learning for prediction and classification problems
- Unsupervised learning for discovering patterns and relationships
- Reinforcement learning for adaptive decision-making based on feedback
Supervised learning is widely used in demand forecasting, fraud detection, and risk assessment. Unsupervised learning supports tasks such as customer segmentation using machine learning and clustering analysis. Reinforcement learning enables systems to learn through trial and feedback, making it useful in dynamic environments such as pricing optimization or automated control systems.
Selecting the right algorithm type allows businesses to align technical approaches with operational needs rather than relying on experimentation alone.
What Benefits Does Machine Learning Bring to Business Decision Making?
Machine Learning enhances business decision-making by analyzing large volumes of data quickly and consistently. It identifies trends, correlations, and patterns that manual analysis may overlook, especially when data complexity increases.
By learning from both historical and real-time data, Machine Learning allows organizations to move from reactive reporting to proactive planning. Instead of asking what happened in the past, businesses can anticipate what is likely to happen next and prepare accordingly.
Machine Learning also reduces dependence on intuition alone. Decisions become evidence-based, measurable, and repeatable. Over time, this leads to improved forecasting accuracy, better customer understanding, reduced inefficiencies, and stronger alignment between strategy and execution.
AI Agents, Knowledge-Based Systems, and Agent Architecture
AI agents are systems that observe their environment, process information, and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents are commonly used in automation platforms, recommendation engines, virtual assistants, and decision-support tools.
A knowledge-based agent relies on stored facts, logical rules, and reasoning mechanisms to make decisions. Instead of relying purely on statistical patterns, these agents use explicit knowledge to determine outcomes. This approach is particularly useful in regulated environments where explainability and consistency are required.
Agent architecture defines how inputs, decision logic, learning mechanisms, and outputs interact. Strong architecture ensures scalability, reliability, and adaptability as business complexity grows. Well-designed AI agents integrate smoothly with existing systems and evolve as organizational needs change.
Neural Networks and Core AI System Components
Neural networks are inspired by the structure of the human brain and consist of interconnected layers that process data step by step. Each layer extracts increasingly complex features, allowing systems to handle unstructured data effectively.
Neural networks are especially effective in areas such as:
- Natural language processing and text understanding
- Image and video recognition
- Speech analysis and voice-based systems
An Artificial Intelligence block diagram typically illustrates how data flows through an AI system. It includes data input layers, processing and learning components, decision logic, and output actions. Understanding these components helps businesses design AI systems that are modular, scalable, and easier to maintain over time.
Clear system architecture reduces implementation challenges and supports long-term expansion.
How Do Planning Components Work in Artificial Intelligence Systems?
Planning enables Artificial Intelligence systems to decide what actions to take and in what order. It connects insight with execution, allowing AI systems to translate predictions into operational decisions.
AI planning involves defining goals, understanding constraints, evaluating possible actions, and selecting optimal paths toward desired outcomes. In business contexts, planning supports areas such as inventory management, workforce scheduling, and resource allocation.
As conditions change, planning systems reassess options and adjust actions dynamically. This adaptability allows AI systems to operate effectively in uncertain environments where static rules would fail.
AI vs Cloud Computing and How Do They Work Together?
Artificial Intelligence and cloud computing serve different but complementary roles. Artificial Intelligence focuses on learning, reasoning, and decision-making, while cloud computing provides the infrastructure required to support these capabilities at scale.
Cloud platforms offer flexible storage, computing power, and deployment environments. AI systems rely on this infrastructure to process large datasets, train Machine Learning models, and deploy applications efficiently across organizations.
When combined, cloud-based services enable businesses to adopt AI incrementally. Teams can experiment, scale solutions, and update models without large upfront investments. This integration makes Artificial Intelligence accessible not only to large enterprises but also to small and mid-sized organizations.
Measuring AI Performance, Accuracy, and Business Impact
Once Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning systems are deployed, measuring their performance becomes essential. Unlike traditional software, AI systems evolve over time as they learn from new data. This makes continuous evaluation a critical part of long-term success.
Performance measurement focuses on how accurately models produce results, how consistently they behave across different scenarios, and how well they align with business objectives. Technical metrics such as accuracy, precision, and recall help evaluate model behavior, while business metrics assess real-world impact such as efficiency gains, cost reduction, or improved customer outcomes.
Monitoring also helps identify model drift, a condition where performance degrades because underlying data patterns change. Regular evaluation ensures that AI systems remain reliable, relevant, and aligned with organizational goals. By connecting technical accuracy with measurable business outcomes, organizations can justify investment and guide future improvements in Artificial Intelligence initiatives.
What Challenges Does Generative AI Face with Respect to Data and Fairness?
Generative AI systems are capable of producing text, images, and other content based on learned patterns. While powerful, these systems face challenges related to data quality, fairness, and reliability.
One major challenge generative AI faces with respect to data is bias. Models are trained on historical data that may reflect social, cultural, or operational imbalances. If not addressed, these biases can influence outputs and lead to unfair or misleading results.
Another limitation is that current generative AI applications do not truly understand meaning or intent. They generate content based on probability rather than reasoning. This makes human oversight essential, particularly in sensitive, high-impact, or regulated business use cases.
How Do Data Strategy and Governance Shape Long-Term AI Adoption?
Successful Artificial Intelligence adoption depends on a strong data strategy. Data must be accurate, accessible, and aligned with business goals to support consistent outcomes.
Data governance defines how data is collected, stored, accessed, and protected. It ensures security, compliance, and trust in AI-driven decisions. Governance also clarifies accountability, helping organizations maintain control over data usage as AI systems scale.
Artificial Intelligence is not a one-time initiative. It is a continuous journey that evolves with data, technology, and organizational maturity. Businesses that invest in strong data foundations, responsible governance, and continuous learning build resilient AI capabilities that support sustainable long-term growth.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning deliver real value when built on strong foundations, clear data flows, and reliable system components. Understanding how AI systems function helps businesses move beyond experimentation toward meaningful outcomes. With the right architecture, governance, and continuous learning, AI becomes scalable and trustworthy. Success depends not just on models, but on how insights are operationalized. Organizations that focus on fundamentals position themselves for long-term, sustainable AI adoption.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How can large companies implement AI systems without downtime?
Use cloud infrastructure and modular deployment. This keeps AI systems running smoothly at scale.
What are the best ways to secure enterprise AI models and data?
Apply role-based access, encryption, and secure storage. Protects both models and sensitive data.
How do organizations monitor AI model performance continuously?
Continuous monitoring tracks accuracy and output quality. Helps catch issues early before they affect results.
What are simple steps for AI governance in businesses?
Set clear rules, accountability, and compliance policies. Ensures responsible and ethical AI use.
How can AI systems learn from real-world business feedback?
Use feedback loops from actual outcomes. This helps models adapt and improve predictions.
How do cloud platforms help scale AI for big enterprises?
Cloud provides flexible computing and storage. Supports large AI workloads efficiently.
What measures ensure AI models remain reliable over time?
Regular monitoring, updates, and validation. Keeps models accurate and dependable.
How can businesses make AI systems trustworthy and scalable?
Combine scalable infrastructure, governance, and feedback. Ensures reliable enterprise AI adoption.


